Using robots driven by AI in surgery is changing the way healthcare is done today. These advanced systems improve accuracy, lower risks, and speed up patient healing. Better accuracy and less invasive methods are made possible by robotic-assisted treatments, which are good for both doctors and patients. Robotic surgery is changing the way complicated medical treatments are done as it becomes more popular.
The Role of AI in Robotic Surgery
Artificial intelligence is a key part of robotic surgery because it lets computers handle huge amounts of medical data, give doctors real-time insights, and help them make decisions. Surgical tools with AI are meant to help surgeons do their jobs better, not take their place. To get the best results from surgeries, these systems use computer vision, machine learning algorithms, and real-time data analysis.
Key Capabilities of AI in Robotic Surgery
- Enhanced Precision: Robotic arms controlled by AI can make tiny moves that humans can't, which lowers the risk of surgery mistakes.
- Real-Time Data Processing: AI algorithms analyze patient data, providing surgeons with real-time insights during procedures.
- Automated Assistance: Robotic systems help doctors with routine jobs, suturing, and tissue handling so that they can focus on more difficult parts of surgery..
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Robotic-assisted surgeries have smaller cuts, which means less pain, fewer scars, and faster healing.
- Improved Visualization: High-definition 3D imaging and augmented reality integration help surgeons see anatomical structures more clearly, reducing risks associated with traditional surgery.
Advantages of AI-Powered Robotic Surgery

Here are some important advantages of AI-Powered Robotic Surgery:
Improved Accuracy and Precision
One of the biggest advantages of AI in surgery is its ability to enhance precision. Robotic arms with AI assistance eliminate hand tremors, allowing for highly accurate movements. It is particularly beneficial for delicate procedures such as neurosurgery and cardiac surgery, where even a minor error can have significant consequences.
Reduced Recovery Time and Complications
Minimally invasive robotic-assisted surgeries result in less trauma to the body. Smaller incisions lead to less blood loss, reduced infection risk, and shorter hospital stays, allowing patients to return to their normal lives faster. Traditional open surgeries often require extensive recovery times, whereas robotic-assisted procedures significantly shorten this period.
Enhanced Surgeon Capabilities
AI and robotics provide surgeons with better visualization, 360-degree movement control, and augmented reality-assisted navigation, which improves their ability to operate in challenging conditions. It is particularly useful in surgeries involving hard-to-reach areas of the body, such as spinal and deep organ procedures.
Lowered Surgical Fatigue
Traditional surgeries can be physically and mentally exhausting for surgeons. AI-powered robots handle repetitive tasks, reducing fatigue and allowing surgeons to maintain peak performance throughout procedures. Long and intricate surgeries can take hours, making human fatigue a significant risk factor. AI helps in reducing strain by automating certain movements, ensuring that the surgeon can focus on critical decisions.
Consistency in Surgical Procedures
Human surgeons, despite their expertise, may have variations in performance due to fatigue, stress, or other factors. AI-driven robotic systems ensure a high level of consistency in each procedure by maintaining a steady hand, precise movements, and programmed accuracy, minimizing the risk of human error.
Better Outcomes for High-Risk Patients
Patients with underlying health conditions such as obesity, heart disease, or diabetes often face increased risks in traditional surgeries. Robotic-assisted surgery offers a safer alternative by reducing complications associated with excessive bleeding, infection, and prolonged anesthesia exposure.
Real-Time Monitoring and Decision Support
AI-enabled robotic systems can monitor vital signs, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and tissue response in real-time. These features help surgeons make data-driven decisions during the procedure, improving overall success rates and patient outcomes.
Leading AI-Powered Robotic Surgery Systems
A few Robotic Surgery Systems are:
Da Vinci Surgical System
One of the most widely recognized robotic-assisted surgical systems, the Da Vinci Surgical System, provides surgeons with enhanced dexterity, precision, and a 3D high-definition view of the operating field. It is commonly used for urological, gynecological, and general surgeries.
Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery
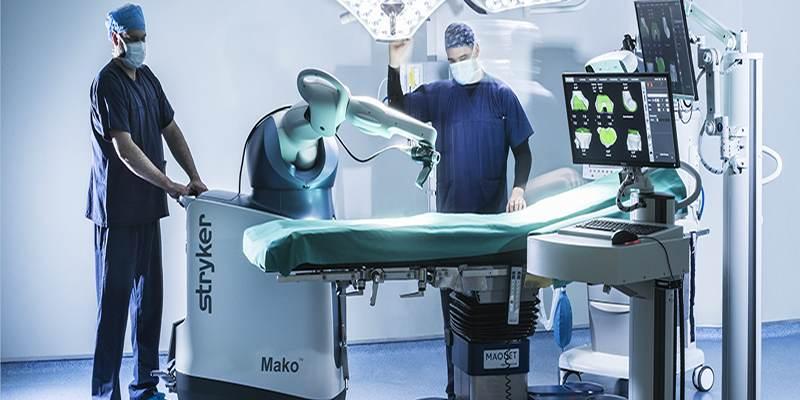
Mako is an advanced robotic system designed for orthopedic procedures, particularly in knee and hip replacements. It enables personalized surgical planning and greater accuracy in joint alignment, ensuring improved long-term mobility for patients.
ROSA Robotic System
ROSA (Robotic Surgical Assistant) is an AI-driven system that assists in neurosurgery and orthopedic procedures, enhancing precision and reducing surgical time. It has proven to be particularly useful in brain surgeries where precision is critical.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the numerous advantages, AI-powered robotic surgery also faces several challenges:
- High Costs: Robotic surgery systems are expensive, leading to accessibility issues for smaller healthcare institutions.
- Training Requirements: Surgeons require specialized training to effectively use robotic systems. Not all hospitals have the resources to provide such training.
- Technical Failures: Like any technology, robotic systems are prone to malfunctions that could disrupt procedures.
- Limited Human Intuition: AI lacks human judgment, making it essential for surgeons to remain in control during critical situations.
- Regulatory and Ethical Concerns: The increased use of AI in surgery raises questions about liability in case of system malfunctions or unexpected complications.
- Limited Adaptability in Emergency Situations: Unlike human surgeons, robotic systems cannot always quickly adapt to sudden, unexpected complications that may arise during surgery.
Conclusion
AI-powered robotic surgery is revolutionizing the healthcare industry, offering unprecedented precision, efficiency, and improved patient outcomes. Robotic-assisted procedures have already proven to be safer, more precise, and less invasive compared to traditional surgical methods. While challenges such as cost, training, and ethical concerns exist, the benefits outweigh the drawbacks, making robotic surgery a key component of modern medicine. By enhancing surgeon capabilities, reducing complications, and improving patient recovery times, AI-powered robotics is reshaping the operating room.
